Endovascular Therapy For Ischemic Stroke
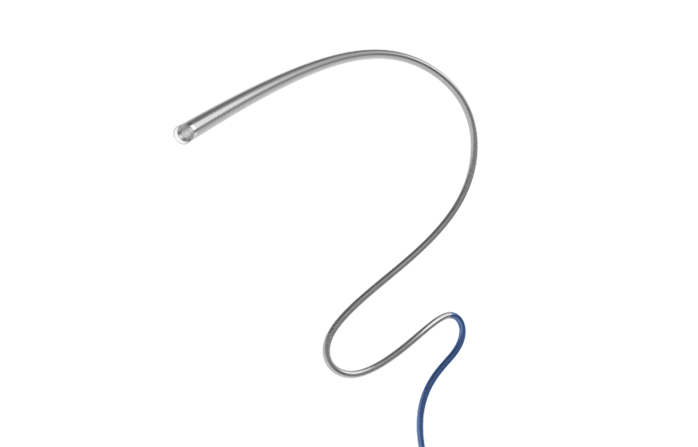
Stent retriever thrombectomy (ACAPT)
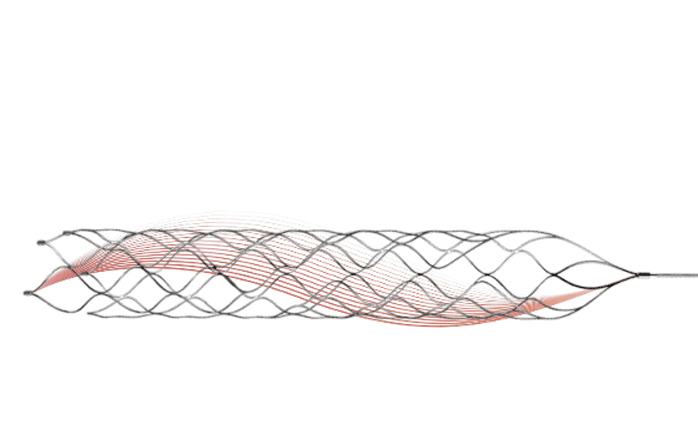
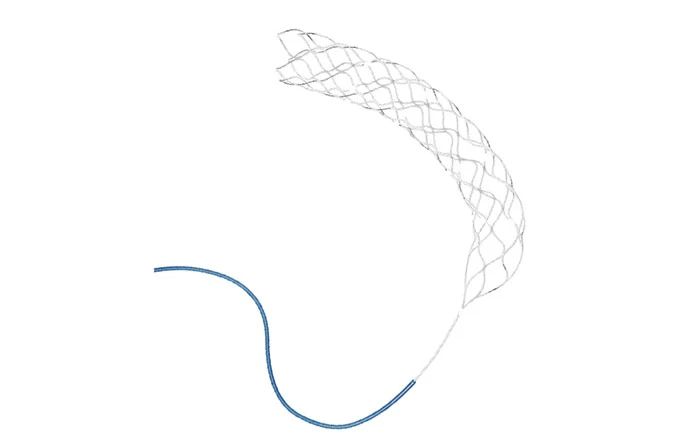
During a mechanical thrombectomy procedure, a stent is firstly compressed in the introductory sheath. After stent navigation to the target vessel, the stent is able to expand and catch the clot upon the microcatheter. Thrombite™ CRD has radiopaque markers at both the proximal and distal ends to allow fluoroscopic visualization, which helps the physician to accurately position the stent retriever to capture the thrombus.
Thrombite™ CRD has an S-shape open-side structure with orderly and staggered arrangement along the spiral direction, which ensures stronger ability to tangle the thrombus. In the stent's circled shape, the spirally rising structure of Thrombite CRD can better capture the clot. Thrombite™ CRD features that all grids at the open side are arranged in a straight line in the longitudinal direction, this structure can wrap the embedded clot more tightly with less possibility to fall off.
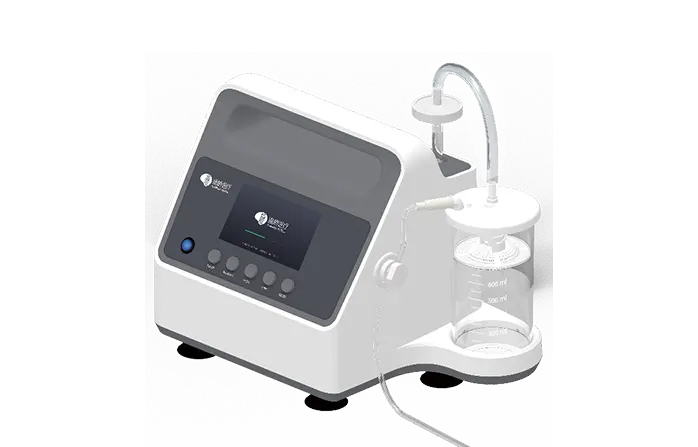
Aspiration thrombectomy (ADAPT)
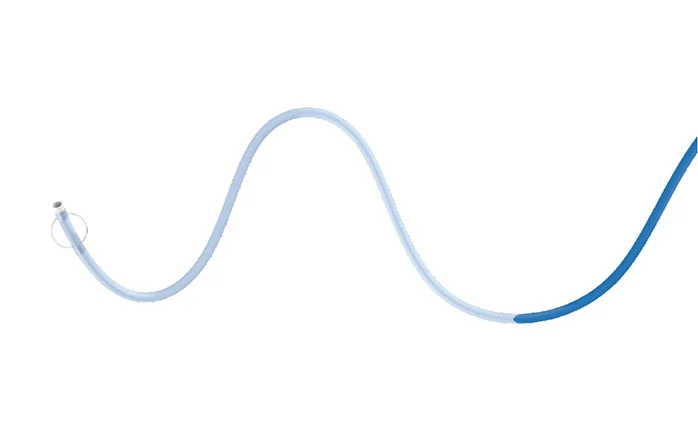
During the treatment, an aspiration catheter is introduced through a guide catheter or introductory sheath. Under fluoroscopic guidance, the aspiration catheter is able to navigate to desired position and provide a stable support lumer for other devices. Alternatively, after the aspiration catheter has reached the lesion, the physician can apply aspiration to extract blood clots out of the body.
Cylone™ aspiration catheter offers excellent suction ability combined with superior navigation of large 0.07" lumen. Under negative pressure, it can maintain a near-vacuum environment to extract thrombus from an occluded artery in the brain. The aspira catheter features a nitinol spiral and stainless steel braided structure with better flatness resistance, and a strengthened arch support design to provide stronger stability and support.